
Quality Falkland Wool Accreditation Scheme
The Farmers Association, in conjunction with the Department of Agriculture (DoA), introduced a quality assurance scheme for the
wool industry. The aim of the voluntary scheme, Quality Falkland Wool (QFW), is to improve the quality of preparation of the national clip through the introduction of specific requirements for infrastructure in woolsheds, standards for preparation and packaging of the wool clip. The DoA acts as an independent body used for accreditation and inspection of the scheme and also provides advice and support to stencil holders.
Since its inception, the scheme has attracted strong support and the number of accredited sheds has reached 35, with more enquiries on joining being received.
Following very well attended wool classing workshops,it was decided that for those growers who are in the QFW scheme and had attended and successfully completed the course, a new stencil would be available to be applied to all bales of wool produced on that property.
It was decided, with approval of the Agricultural Advisory Committee, that QFW farms would self-audit before the shearing season commenced and DoA staff would visit where applicable. All farms that self-audit and return their completed forms to the DoA are issued a certificate to display in their shearing sheds. This indicates that the grower and farm fully comply with the guidelines set down in the QFW standards.
With growing pressure worldwide to improve and project wool as a more versatile and competitive product, the importance of wool preparation and correct handling is constantly growing. Therefore, bales without a quality assurance stencil do not give buyers the confidence that the wool is prepared to any set standards, whereas Falkland Island bales bearing the QFW logo give buyers confidence that the wool is prepared to a consistently high and uniform level.
The QFW is currently under review. If you would like to know more about QFW or are intrested in joining please contact the DoA.

Laboratory Services

The Department of Agriculture has a large and well equipped laboratory. It is the responsiblity of the laboratory for the processing of all soil and animal feed samples, along with faecial egg counting (FEC).
Soil samples are analysed for a wide range of nutrients including NPK (nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium), trace elements and exchangeable cations (calcium, magnesium, potassium and sodium).
The laboratory assists with the preparation of fish/squid samples for bacteriology tests. These samples are carried out by the public health laboratory at the Stanley hospital.
Fish samples are also sent to the UK laboratories of the Government Chemist for heavy metal/PCB tests.
The laboratory also provides support to the Veterinary Services section with animal disease diagnosis and runs tests such as haematology profiles on blood samples, preparation of blood for biochemistry screening at the hospital and parasitological testing of faeces samples (mainly sheep and cattle).
Soil and Plant testing
In the DoA Laboratory we can provide analytical testing on soil samples to provide information on the chemical properties of the soil.
As a basic package we offer pH and NPK testing:
To test for pH we use a pH probe and test soil suspension in Water, Calcium Chloride, and Potassium Chloride, this gives us values that allow us to provide insight into the in situ soil pH, the Sodium content of the soil and cation saturation.
When testing for N (Nitrogen) we use the Kjeldahl method to determine the total Nitrogen content of the soil.
To test for P (Phosphorous) the laboratory uses the Bray I method to give a value for the exchangeable Phosphorous in the soil, however this can be easily modified to the Bray II method to give total Phosperous although this is not recommended as only the exchangeable Phosperous is available for plants to use.
Testing for K (Potassium) is done through flame photometry where extractable potassium is removed in to solution using Ammonium Nitrate and the levels of potassium are then determined by linear regression using a standard solution of Potassium Salt.
The Laboratory also offer tests for Sodium, Organic matter and Basic Cation Exchange capacity.
Feed Testing
Feed testing is only required if you are growing your own feed for livestock such as turnips, or potatoes.
The DoA laboratory can offer Feed tests for:
Metabolic energy, which is determined as a function of the Digestibility of Organic Dry Matter. The Metabolic Energy is an estimate of the energy that is available for use by the animal.
Dry matter, this is a measure of how much of the feed is not water, and is determined by the removal of all water from the sample.
Dry Matter Digestibility, this provides us with a prediction of the amount of the feed that may be digested by a ruminant, we achieve this through the Pepsin-Cellulose method which seeks to imitate the digestive track of Ruminants.
Crude Protein, this is determined through the Kjeldahl method. Crude Protein is a measure of the total Nitrogen in the plant which is the building block of all amino acids which make up all proteins.
Neutral Detergent Fibre, which is determined through the digestion of feed material in a neutral solution. Neutral detergent fibre is a measure of most fibre in a plant.
Phosphorous, which is a key building block of DNA and ATP both of which are vital for life to grow and exist, it is determined through the same method as used in Soil Testing.
Blood and Tissue Testing
The laboratory can also perform haematological testing, and in vitro clinical chemical analysis if requested to do so by the veterinary services as well as hydatid checks on suspect samples from animals.
Other tests such as heavy metals, trace elements, and some blood and serum tests are sent overseas for testing in specialised laboratories.
FEC (Faecal egg count)
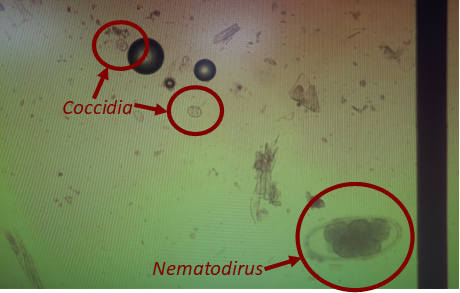 The testing of animal faeces for the presence and quantity of parasite eggs is a helpful tool to determine if there is a need for worming treatment. The Veterinary Service and DoA are able to help do this by carrying out Faecal Egg Counts (FEC) on suitable samples from Sheep, Cattle, and Horses.
The testing of animal faeces for the presence and quantity of parasite eggs is a helpful tool to determine if there is a need for worming treatment. The Veterinary Service and DoA are able to help do this by carrying out Faecal Egg Counts (FEC) on suitable samples from Sheep, Cattle, and Horses.
FEC’s should be booked in with the Lab by contacting the Lab Scientist by email or phone.
Samples should be dropped off at the DoA no later than 48 hours after collection and should be stored in the fridge except when in transit, a sample submission form should be dropped off at this point too, these are available for download from our website. Samples should only be submitted on a Monday, Tuesday or Wednesday to allow for time to process them in that week.
Please ensure that samples are left with a staff member and not on the doorstep.
The DoA Laboratory Service now has a new online booking system that can be used to book FEC samples in to the Lab, it can be found on the DoA Lab Booking Website
Researchers
The DoA laboratory can provide space for scientific researchers to undertake laboratory research, and experimentation, as well as providing guidance and training on how to use the equipment available in the laboratory.
Researchers are required to complete a laboratory access form and review and add to a risk assessment both of which can be requested form the Laboratory Scientist. More guidance can be found in the Guidance for Visiting User’s document available for download below.
The DoA Laboratory Service now has a new online booking system that can be used to book space in the DoA Laboratory, it can be found on the DoA Lab Booking Website and reserchers must book there space through the Site to ensure that the space is avlible to them.
FEC (fecal egg count):
Soil Samples:
Feed Samples:
Researchers Information:
Joshua Anderson-Wheatley | Laboratory Scientist
Department of Agriculture | Falkland Islands Government | Stanley | Falkland Islands | FIQQ 1ZZ
Tel: +500 27355 | Fax: +500 27352 | E-mail: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. | Facebook: Falkland-Islands-Government-Department-of-Agriculture
Follow @FalklandsGov on Twitter | Like the ‘Falkland Islands Government’ Facebook page | Follow @Falklands_Gov on Instagram | Subscribe to our YouTube Channel
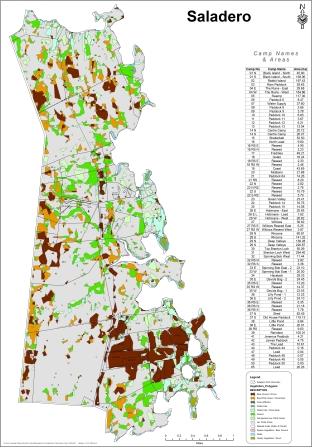
Farm Mapping
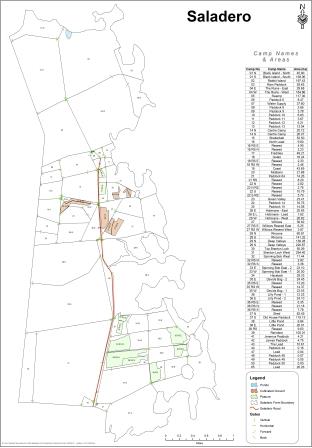
The Department of Agriculture is continuously providing and expanding the services offered to farmers through the Farm Mapping project, which can be a useful tool in farm and land management.
The DoA holds external farm boundary data and using a GPS to mark internal fence lines and other farm features which can then be displayed on a map and then used in other mapping calculations and features.
Other information such as corrals, leads, water sources, ditches and areas of interest can be recorded on a GPS unit and used in farm maps.
Using this, the DoA can provide farmers with accurate fence-line data and paddock sizes which is a key tool for assisting in grazing management systems. Farmers can use the information to plan and budget for new fencing and pasture and cropping works.
GPS units, outline farm maps and a tutorial on the process are available from the DoA and staff are continuously developing the mapping services available.
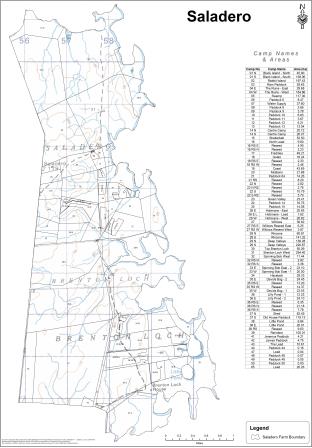
Four layers of data are commonly used when creating farm maps:
1. External farm boundary data collected by the Public Works Department Design Office, with an accuracy of one metre or less
2. Internal fence line data collected by farmers using handheld GPS units, which have a maximum accuracy of four metres
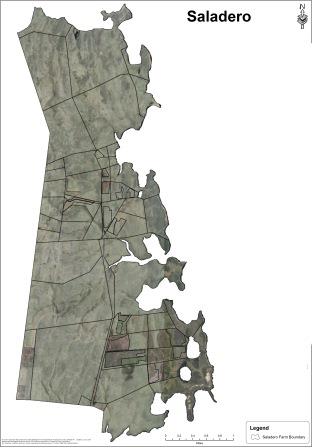
3. A vegetation classification layer with data supplied by two Landsat 7 Images (captured between January 2001 and March 2002), processed at Queens University Belfast after ground truthing was used to identify vegetation types. The Falkland Islands vegetation was divided into nine broad vegetation classes. Vegetation classes are based on a number of sample areas and this data was extrapolated to give Island-wide vegetation analysis. The images, one of East Falkland and one of West Falkland, have a fifteen metre pixel resolution
4. The fourth layer consists of scanned images, digitally referenced, of the twenty nine Ordinance Survey maps at 1:50,000 scale.
As part of the development of the farm mapping service, the DoA has been working closely with the South Atlantic Environmental Research Institute (SAERI) who have employed a GIS Specialist and the DoA are now pleased to also be offering maps which feature Google Earth™ imagery.
The DoA and SAERI are also working with Queens University Belfast using soil sampled analysed by the DoA to produce some of the first detail soil mapping data of the Falkland Islands.
Core Sampling
Background and Information
In 1999 the Department of Agriculture (DoA) set up a link with the New Zealand Wool Testing Authority (NZWTA) to be their accredited representatives to oversee the core sampling of Falkland Islands bales of wool. The DoA currently has 4 qualified wool sampling officers certified by the NZWTA.
oversee the core sampling of Falkland Islands bales of wool. The DoA currently has 4 qualified wool sampling officers certified by the NZWTA.
The information gained from the testing of core samples is used to generate a legally binding document that enables growers to sell their product worldwide, it is know as an IWTO Pre-Sale Test Certificate.
The criteria shown on the Pre-Sale Certificate are;
- mean fibre diameter
- yield (Schlumberger Dry)
- colour
- vegetable matter
- gross mass
- tare
- net mass
- total bales
- bale numbers
Benefits of coring locally;
- Opens up the to sell wool to a greater number of destinations
- Sell it in the international market place and gain a price for their product that is based on world market indicators
- To rationalise wool freight logisitics
- To increase flexibility as to time of selling
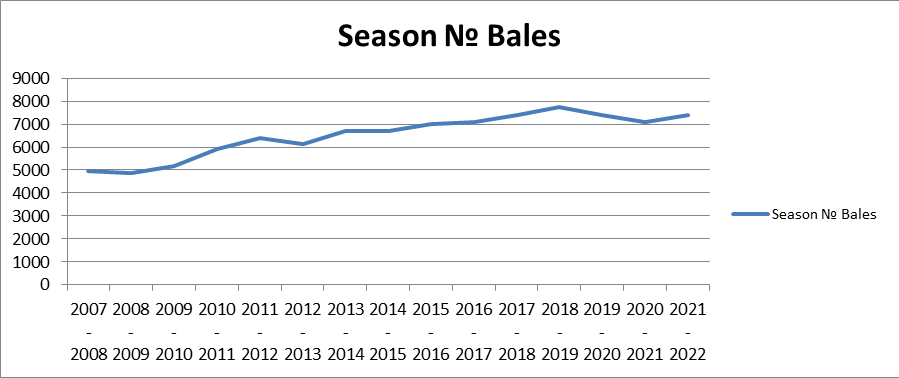
Trends
In the first year growers were cautious of this new service and only 726 bales were manually cored. Over the years interest has increased, this last season (2021/22) saw 7399 bales cored.
Grab Sampling
There is also the opportunity to grab sample bales. The main purpose of grab sampling is the test the length and strength (L&S) of the staple and Position of Break (PoB) within the staple. In counties that sell wool by auction the grab sample is also used for display to let potential buyers see and feel the quality of the wool. Only main lines of wool tend to get grab sampled.
Looking Forward
The current wool warehouse is situated on FIPASS, a floating dock, which is due for imminent demolition. A new purpose built wool warehouse will be situated on dry land with hard standing for trucks to unload and turn around, load and stack containers, office space and new semi-automatic core and grab machine. It is envisaged that this new facility will improve throughput and efficiency of handling and testing of wool bales for Falkland Island farmers.
For more information on coring please contact This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it..

